Author: Jonathan Vila
Original post on Foojay: Read More
Table of Contents
The Problem: Local Skills vs. The Cloud  What is MCP technology?Let me introduce you to SonarQube MCP Server?
What is MCP technology?Let me introduce you to SonarQube MCP Server?  Tools Provided by the SonarQube MCP ServerHow to install the SonarQube MCP server in WindsurfExample: Analyzing a snippet with analyze_code_snippet toolConclusion: Agentic Superpowers
Tools Provided by the SonarQube MCP ServerHow to install the SonarQube MCP server in WindsurfExample: Analyzing a snippet with analyze_code_snippet toolConclusion: Agentic Superpowers 
Hola! 👋 As a Java developer, you probably spend a good chunk of your day making sure your code doesn’t just “work,” but is also maintainable, secure, and reliable. I’ve been using a tool that is changing how I handle large projects: Windsurf.
It is an agentic IDE that understands what you are trying to do across your whole project. Let’s see why this is a game-changer for our Java workflows. 🚀
What is Windsurf AI?
Windsurf is an AI-powered IDE developed by the team at Codeium. You can find it at windsurf.com. While it feels familiar because it is built on the VS Code foundation, it is designed from the ground up to be “agentic”.
Unlike tools that just sit in a side panel, Windsurf is deeply integrated into the editor. Its core engine, called Cascade, has a deep understanding of your entire codebase. It doesn’t just look at the file you are typing in; it understands the relationships between your Spring services, your DTOs, and your repository interfaces.
Main characteristics that make Windsurf different
What makes this IDE stand out from other tools is how it handles “Flows”:
- Action-Oriented Agent: It can perform tasks like running mvn test, creating new files, or debugging a stack trace by itself.
- Unified Flow: You don’t have to copy-paste code. You work alongside the agent in “Write Mode,” where it can directly apply changes to your files while you watch.
- Real-time Awareness (Flow State) : Cascade is aware of your real-time actions in the editor—no need to re-prompt with context about what you just did. Simply say “Continue” and it picks up where you left off.
- Deep Context Engine : Windsurf uses an optimized RAG approach with proprietary M-Query techniques to index your entire codebase, open files, terminal activity, clipboard, and even your recent code changes for highly relevant suggestions.
- Fast Context with SWE-grep : A specialized subagent retrieves relevant code up to 20x faster than traditional agentic search using custom SWE-grep models trained for rapid parallel code retrieval.
- Windsurf Tab (Supercomplete) : A custom in-house model powers diff-aware suggestions that can edit before and after your cursor, plus “Tab to Jump” and “Tab to Import” features for seamless navigation.
- Named Checkpoints & Reverts : Create named snapshots of your project state and easily revert Cascade’s changes to any previous step.
- Built-in Planning Agent : A specialized planning agent continuously refines long-term plans while your selected model handles short-term actions.
The Usual Flow and the “Verification” Problem
In a typical flow, you ask the agent: “Create a REST controller for managing Books.” The agent generates the code, and it looks good. But how do you know it follows your team’s quality standards? 🧐
Usually, you would have to manually run a scan, wait for the results, and then tell the agent: “Hey, SonarQube says this method has a cognitive complexity issue, fix it.” This back-and-forth is slow and breaks your “flow state”. This is exactly the problem Agent Skills aim to solve.
What are Agent Skills?
Agent Skills are reusable sets of instructions and procedural knowledge that you give to the agent to resolve specific problems. Technically, a Skill is a folder containing a SKILL.md file with specific instructions and, optionally, scripts or reference files to tackle concrete problems.
Example: A Skill with Command Execution
You can create a skill that tells the agent how to run a local script to verify a snippet against a SonarQube instance using its API through a client that will send a request to SonarQube API.
The Skill definition (SKILL.md):
# sonar-verify-snippet Description: Use this skill to verify the quality of a Java code snippet. Instructions: 1. Execute the local script: `./scripts/sonar-check.sh` passing the code snippet as a parameter. 3. Read the output from the command line. 4. If errors are reported, refactor the code and repeat until it passes.
How skills look like in Windsurf:
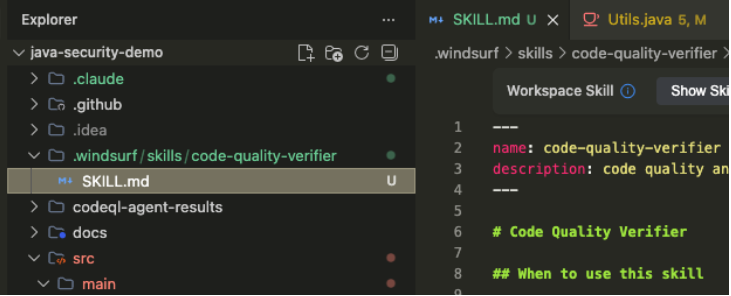
The Problem: Local Skills vs. The Cloud ☁️
Skills are powerful, but they have a “spatial” limitation: they need to be stored locally in your project or IDE configuration.
If you work across different machines or teams, managing these local files becomes a headache. Also, if the logic to connect to SonarQube is complex, you don’t want a massive script sitting in every project folder. This is where we need something that can run anywhere—even remotely—without leaving a local trace. Enter MCP servers.
What is MCP technology?
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is an open standard that acts like a universal connector for AI agents.
Benefits:
- Standardization: Any tool that speaks MCP can connect to Windsurf instantly.
- Remote or Local: Unlike Skills, MCP servers can run as remote services or local Docker containers.
- No Local Trace: You don’t need to clutter your repo with script files; the agent just talks to the MCP endpoint.
The adaptability of the MCP standard means that a Windsurf agent isn’t limited to just one system. Beyond the crucial SonarQube MCP Server for static analysis, agents can be empowered with connections to other enterprise tools. Common MCP servers include the Jira MCP Server (enabling the agent to read/update tickets and synchronize tasks), and the OpenAPI MCP Server (allowing the agent to interact with internal APIs), among hundreds. This ability to connect to diverse, specialized servers makes the Agent a truly versatile orchestrator of development workflow.
Let me introduce you to SonarQube MCP Server? 👋
The SonarQube MCP Server is a specialized remote service designed to bridge the powerful code analysis capabilities of SonarQube directly into the Windsurf agentic IDE via the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
It acts as a secure, stateless middleware, allowing the Windsurf agent (Cascade) to communicate with a designated SonarQube Cloud or Server environment without needing to install complex client libraries or massive scripts within the local project repository. By running typically as a Docker container, it encapsulates all the necessary logic—authentication, API communication, and issue parsing—for interacting with SonarQube’s Web API.
This remote approach resolves the “local trace” problem associated with Agent Skills, enabling consistent, enterprise-grade code quality checks across all developer environments.
Tools Provided by the SonarQube MCP Server
Once the SonarQube MCP Server is configured and active in Windsurf, it exposes a set of “tools” or specialized functions that the Cascade agent can autonomously invoke. These tools are the agent’s new capabilities for interacting with code quality.
The SonarQube MCP server provides 25 distinct tools for agent interaction at the time of this writing. The most commonly used tools include:
| Tool Name | Description | Agentic Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| analyze_code_snippet | Analyzes a specific code fragment for quality issues and vulnerabilities. | Example: Highlighting a new method and asking the agent to “ensure this passes Sonar checks.” |
| search_sonar_issues_in_projects | Retrieves a list of all current, active issues for the entire codebase (project). | Example: The agent autonomously generating a task list for the developer based on critical “blocker” issues. |
| show_rule | Allows the agent to query the SonarQube rule set to get all details for a given rule. | Example: The agent verifying full details on a given rule (e.g., maximum line length) and its properties. |
| change_sonar_issue_status | Enables the agent to mark an issue as “False Positive” or “Accept” via the API. | Example: The agent marking a known issue as “Accepted Debt” after discussion with the developer. |
How to install the SonarQube MCP server in Windsurf
To bring Code Quality checks into Windsurf via MCP, you can use Docker:
1. Generate a Token: In your Sonar instance, generate a “User Token”.
2. Manual vs Automatic installation
Automatic: In Windsurf, go to Settings > Cascade > MCP Servers.
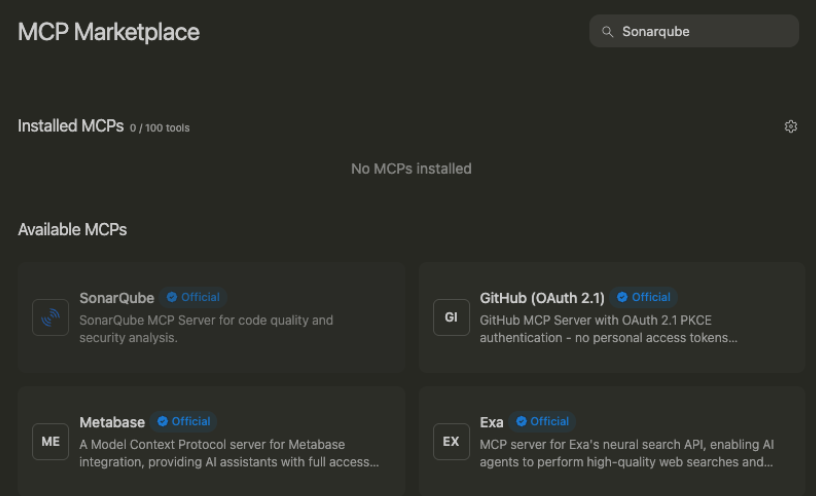
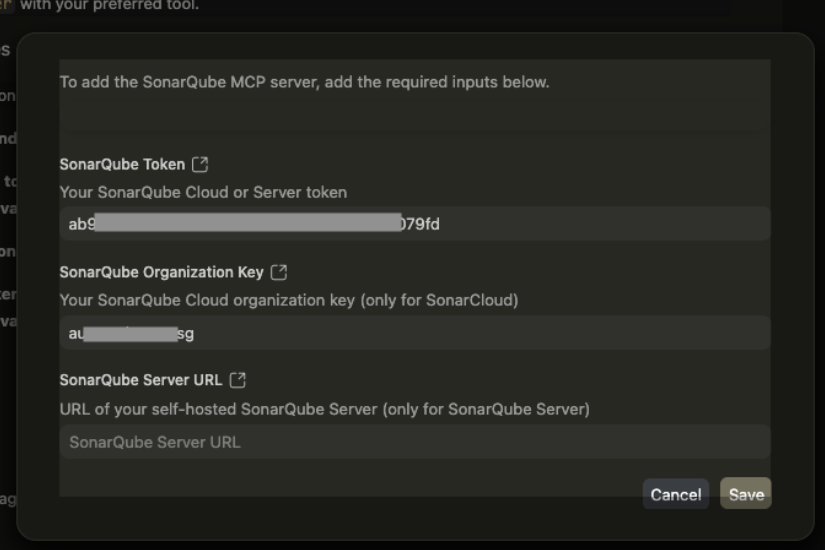
Manual: Add this to your ~/.codeium/windsurf/mcp_config.json file.
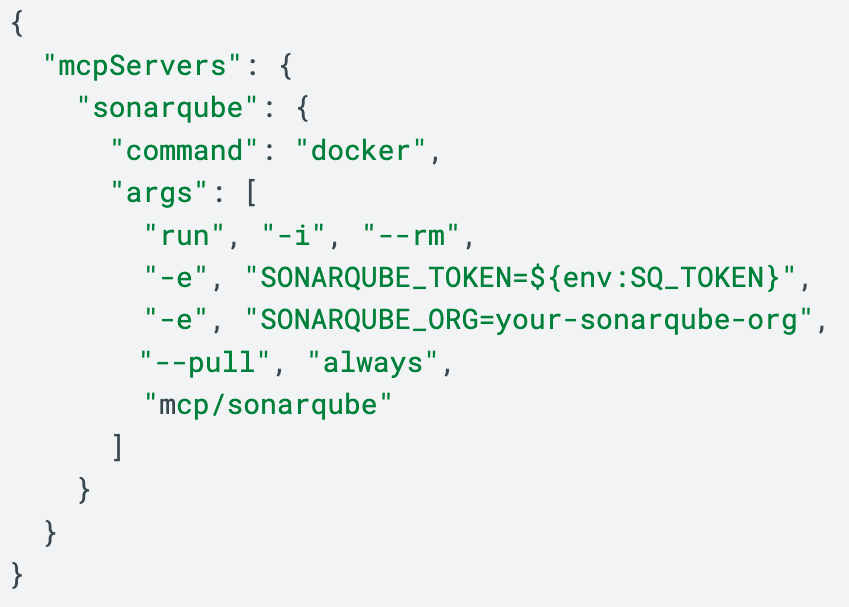
Or even easier, using the free extension SonarQube for IDE, that you can install in major IDEs like VSCode or IntelliJ, you will have live analysis results on your IDE, plus a very convenient way to install SonarQube MCP server or even Windsurf Hooks to guarantee that all responses from the Agent go through a SonarQube analysis.
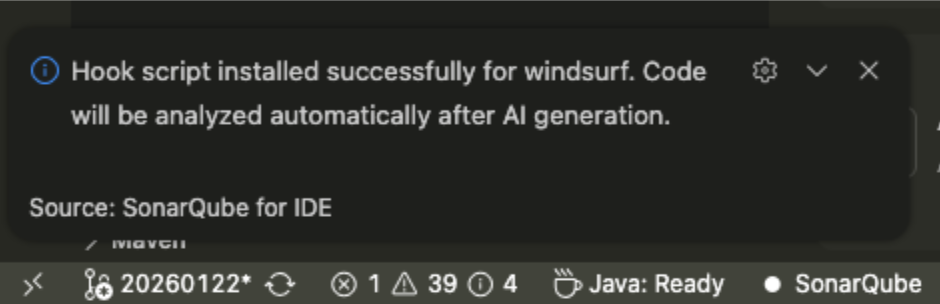
Example: Analyzing a snippet with analyze_code_snippet tool
Once the SonarQube MCP server is active, Windsurf has a new “tool” called analyze_code_snippet, among other 24 tools to interact with SonarQube.You can highlight a Java method and tell Cascade: “@Utils.java#L22-31 Analyze this with Sonar and fix it.”
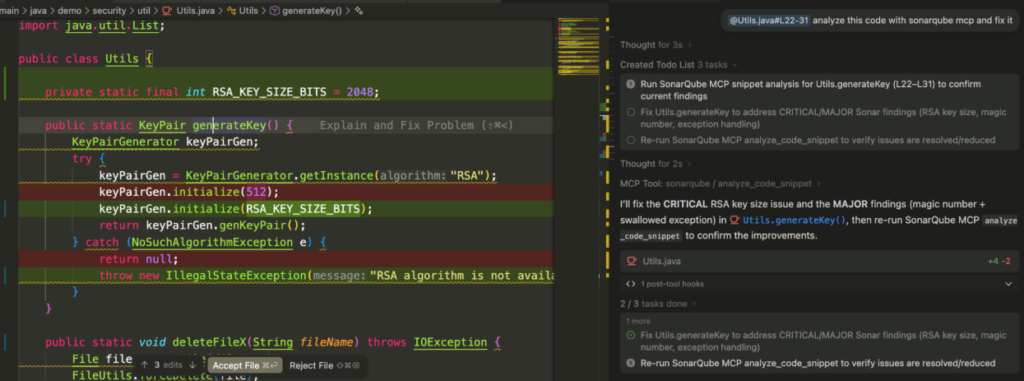
The Agent does the following:
- Sends the snippet to the SonarQube MCP server.
- The server checks the code and returns the issues (e.g., “Use a logger instead of System.out”).
- Cascade will potentially fix the code in your editor automatically.
// Before:
public void logInfo(String msg) {
System.out.println("LOG: " + msg); // Issue!
}
// After Cascade + MCP fix:
public void logInfo(String msg) {
logger.info("LOG: {}", msg); // Better!
}
Conclusion: Agentic Superpowers 🦸♂️
By supporting both Skills and MCP, Windsurf gives us the best of both worlds. You can use Skills for quick, project-specific local automations, and MCP to connect your agent to powerful, remote platforms like SonarQube.This combination turns the IDE from a simple text editor into a true AI partner that ensures your Code Quality is top-notch without you having to lift a finger.
The post 🌊 Windsurf AI + Sonar: The Agentic Dream Team for Java Devs 🚀 appeared first on foojay.
 NLJUG – Nederlandse Java User Group NLJUG – de Nederlandse Java User Group – is opgericht in 2003. De NLJUG verenigt software ontwikkelaars, architecten, ICT managers, studenten, new media developers en haar businesspartners met algemene interesse in alle aspecten van Java Technology.
NLJUG – Nederlandse Java User Group NLJUG – de Nederlandse Java User Group – is opgericht in 2003. De NLJUG verenigt software ontwikkelaars, architecten, ICT managers, studenten, new media developers en haar businesspartners met algemene interesse in alle aspecten van Java Technology.