Author: Jonathan Vila
Original post on Foojay: Read More
Table of Contents
Hola Java developers! 👋
Welcome to the Grand Finale of our series.
- Part 1: We turned your IDE into a fortress.
- Part 2: We synced the team with Connected Mode.
- Part 3: We secured the Supply Chain (dependencies).
We have become excellent at finding bugs. But let’s be honest: Finding them is only half the battle. Who is going to fix them?
We are drowning in a backlog of “Technical Debt,” “Code Smells,” and “Security Hotspots.” You don’t have enough hours in the day to refactor every complex method or research the perfect fix for a regex denial-of-service vulnerability.
This is Part 4. Today, we stop “finding” and start “auto-remediating” using the new AI superpowers in SonarQube.
Problem #1: “I see the bug, but I’m too lazy (or busy) to fix it”
You are in IntelliJ. SonarQube highlights a block of code with high Cognitive Complexity.
You sigh. You know you should refactor it, but untangling those nested if/else statements will take you 20 minutes, and you have a deadline. So, you ignore it.
The Solution: AI CodeFix (The “Magic Button”).
SonarQube is no longer just a spellchecker; it is an autocorrect.
Whether you are in IntelliJ (via Connected Mode) or reviewing a Pull Request in the SonarQube dashboard, you will see a new button: “Generate AI Fix”.
- How it works: It analyzes the specific issue and your code context using a deterministic static code analysis and it creates a fix using an LLM (like GPT-4o).
- The Result: It proposes a complete code change that fixes the bug without breaking the logic.
- Your Job: You just review the diff and click “Apply”.
What used to take 20 minutes of refactoring now takes 10 seconds of reviewing.
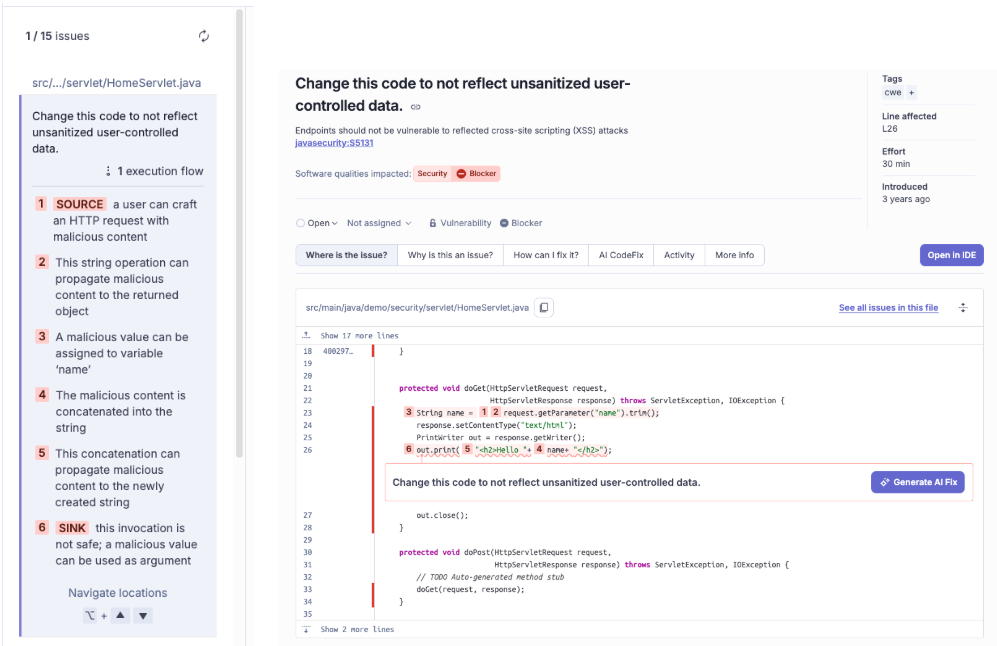
We can see here the issue and the execution flow, and the “Generate AI Fix” button
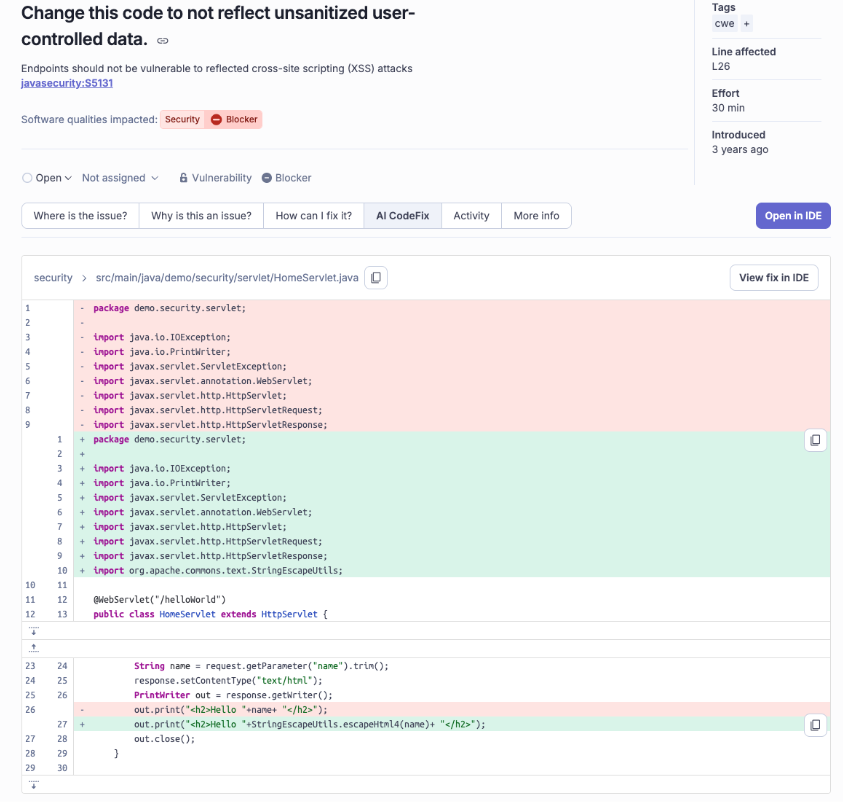
And the solution suggested by SonarQube AI CodeFix feature

And finally this is the way we see the change coming from SonarQube AI CodeFix in IntelliJ IDE
Problem #2: “My AI Assistant writes buggy code because it doesn’t know our rules”
You are using Cursor, Windsurf, or Claude Desktop to generate a new Spring Boot Service.
The AI writes valid Java code, but it violates some specific rules:
- “Don’t use Field Injection.”
- “Always use the var keyword.”
- “Copyright headers must be present.”
You copy-paste the AI code, and immediately, SonarQube yells at you. You waste time fixing what the AI messed up.
The Solution: SonarQube MCP Server (Model Context Protocol).
This is a game-changer. MCP is an open standard that allows AI Assistants (like Claude or Cursor) to “talk” to your tools.
By enabling the SonarQube MCP Server, you are effectively giving your AI Assistant the confidence of deterministic tools.
Before generating code, your AI agent can query SonarQube to understand the active rules and project context.
- The Scenario: You ask Cursor: “Refactor this class.”
- The Background Magic: Cursor asks SonarQube: “What are the rules for this project?”
- The Outcome: The AI generates code that is already compliant with your Quality Profile. No red squiggles. No rework.
Read these extended articles about MCP , SonarQube MCP Server and MCP Security pitfalls.
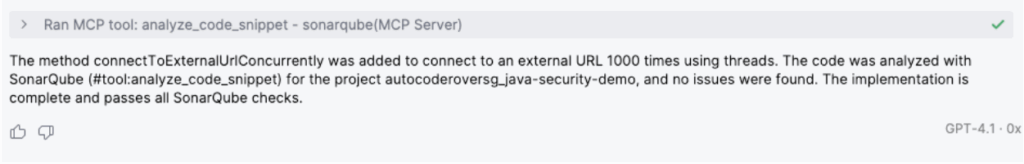
Asking the agent to produce code but connecting it to SonarQube MCP Server in order to be sure it doesn’t contain issues.
Problem #3: “How do I know if this Project with AI-generated code is actually good?”
Your team is using GitHub Copilot heavily. Productivity is up 30%. But… are they generating high-quality code, or just generating more bugs faster?
The “Black Box” of AI code is a major anxiety for Tech Leads.
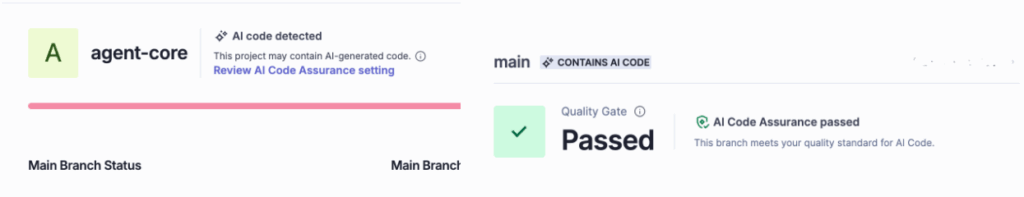
The Solution: AI Code Assurance.
SonarQube allows you to tag projects that use Generative AI or Autodetects AI-generated content (at the moment only considering Github Copilot projects). It then enforces a specific, stricter “AI Code Assurance” process.
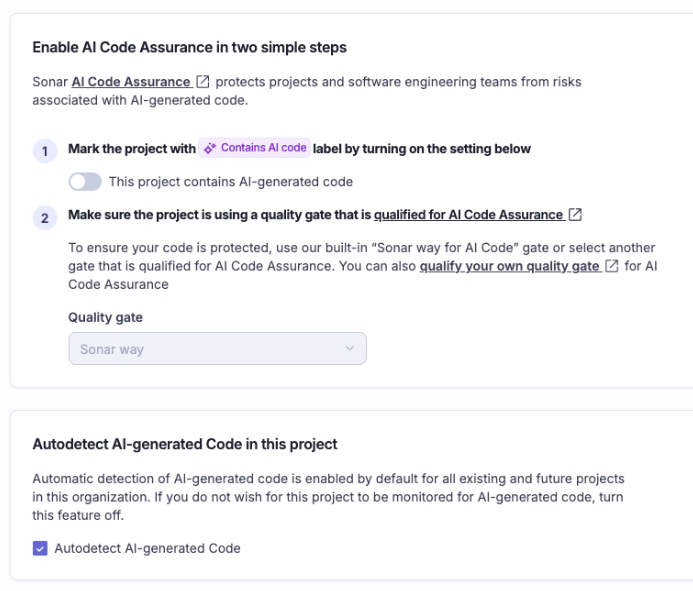
It will assign the “Sonar way” quality profile to the project, that checks for:
- No New Issues: Zero tolerance for bugs in AI code.
- Security: All hotspots must be reviewed (AI loves to hallucinate insecure config).
- Tests: High coverage requirements (because AI code is only as good as its tests).
When a project passes this strict gate, it earns the “AI Code Assurance” badge. It’s a seal of approval that tells management: “Yes, we used AI, and yes, we verified it’s safe.”
🎯 Series Summary: The Complete Cycle
We have come a long way.
- Part 1 (The Developer): We installed SonarQube for IDE to catch bugs locally.
- Part 2 (The Team): We used Connected Mode to sync rules and enforce Quality Gates in CI/CD.
- Part 3 (The Supply Chain): We used Advanced Security to catch vulnerable dependencies and deep injection attacks.
- Part 4 (The Future): We used AI CodeFix and MCP to automate the cleanup and guide our AI assistants.
The Conclusion?
Quality is not about slowing down to fix bugs.
It’s about building a pipeline where the IDE coaches you, the Server protects you, and the AI can help you.
Stop fixing bugs on Fridays. Let the tools do the work, so you can focus on building the next big feature.
Happy Coding! 🚀☕️
The post 🚀 The Future is Now: AI Code Assurance and MCP with SonarQube (Part 4) appeared first on foojay.
 NLJUG – Nederlandse Java User Group NLJUG – de Nederlandse Java User Group – is opgericht in 2003. De NLJUG verenigt software ontwikkelaars, architecten, ICT managers, studenten, new media developers en haar businesspartners met algemene interesse in alle aspecten van Java Technology.
NLJUG – Nederlandse Java User Group NLJUG – de Nederlandse Java User Group – is opgericht in 2003. De NLJUG verenigt software ontwikkelaars, architecten, ICT managers, studenten, new media developers en haar businesspartners met algemene interesse in alle aspecten van Java Technology.
 Series Summary: The Complete Cycle
Series Summary: The Complete Cycle